Harzevil Environment Revitalization project
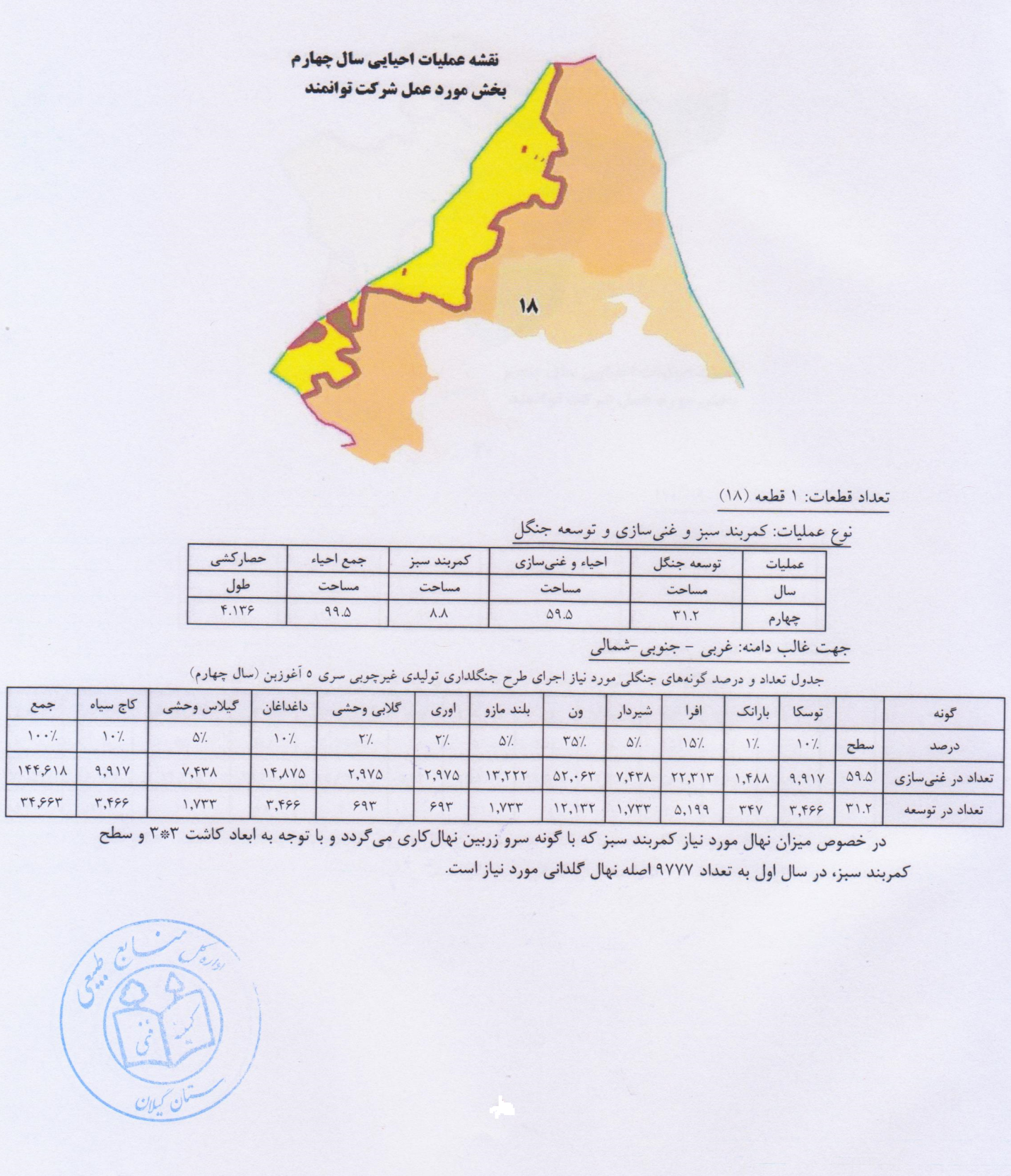
Aghuzbon 5 series non-wood production forestry project is located in the southern and southeastern heights of Rudbar city and in terms of division of forestry areas, it is located in the 20 Seydan watershed. In terms of administrative and national divisions, it is located in the field of natural resources and watershed management of Rudbar city. Its distance to Rudbar city is about 3 km. The forests of this series are located at an altitude of 220-2530 meters above sea level from the north to the villages of Nasfi, Aghozban and forests of series 4 Khas Kool, from the east to series 4 Khas Kool and series 3 Seydan and from the west to the upper settlements of Rudbar city is limited to the skyscraper pastures from the south. Parcels 18, 19 and 20 of the non-wood forestry production plan of 5 series of Oghuzban with an area of 752 hectares, is the area in environment revisedialtion project
From the beginning of the universe, nature has been the bedrock of human life and from the very beginning, human beings have depended on it to satisfy all their wants and needs. In the initial stage, due to the small human population, human intervention was balanced and interference in its field could not cause a structural change in its overall appearance. But today, due to the increasing population growth, the unbridled development of technology and being in the post-industrial age, which has faced human societies on the one hand with limited natural resources on the other hand with environmental pollution, has become more visible. The role and position of forests is not hidden from anyone due to its many and varied values. Forests are not only the greenery and beauty of nature, but also provide the necessary air for human life by absorbing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen. Forests not only prevent floods, but also prevent soil erosion by storing water from snowmelt and rain, and by stabilizing the ozone layer, reduce the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation and the diseases caused by it. Control of plant pests and diseases and prevent the invasion of invasive species to agricultural products, the emergence of aesthetic and artistic values, production of non-wood products, the possibility of side activities such as aquaculture, production of edible mushrooms and providing tourism and many benefits. Other valuable achievements are the blessings that come to the living beings of the earth.
Today, despite the fact that the vital importance of the forest is becoming clear to everyone, its area is constantly decreasing. Due to unreasonable interventions, significant parts of the forest levels have been decommissioned. The intensity of these interventions in some areas is so destructive that they are forced to become areas of protection and protection. Unfortunately, the narrow strip of northern forests is being destroyed and encroached upon for various reasons by ranchers on the summer side, by farmers on the plain side, and by forest dwellers on the inside. Surveys and statistics show that the amount of inventory per hectare has decreased significantly compared to previous decades. In order to solve the problem, it is necessary to take more serious measures in the field of protection and by using management sciences and techniques and intervening in the quality of existing masses, increase the productive capacity of forests, thereby increasing productivity per unit of forest income. increased. Aghuzban 5 series forests are located from the watershed No. 20 of Seydan with an area of 5782 hectares at the end against the Hyrcanian forests. From the north it is limited to the lands and possessions and settlements of Barehsar, Mashin Khaneh, Dosalen and Drazchal, from the south to the summer pastures, from the east to the summer pastures and pastures of Ghoushalneh and Damash from the west to the 9 Liavel series forests. Exploitation has led to the removal of all native trees by implementing the method of complete felling in previous years and for the purpose of charcoal (approximately 72-82 years ago). The tree bases of the forest mass are mostly young and in the vegetative stage are beams and beams and sometimes loose. In terms of mass fusion, it is seen as pure beech. In terms of number, about 95% of it is beech and some bases of hornbeam, oak and alder (at the edge of the valley) can be seen. Due to the special condition of the habitat and the existence of a cold climate with a short growing season, maintaining existing forests as a supportive green belt is extremely valuable. On the other hand, developing countries’ access to new energy sources is essential for their economic development. Jadid has shown that there is a direct relationship between a country’s level of development and its energy consumption. Given the limited reserves of fossil energy and the increasing level of energy consumption in the current world, it is no longer possible to rely solely on existing energy sources.
In our country, due to the increasing need for energy resources and the depletion of fossil energy resources, the need to keep the environment healthy and reduce air pollution, the use of new energies such as wind energy, solar energy, hydrogen, energy in the ground can have a special place. .
Today, political and economic crises and issues such as limited fossil fuel sustainability, environmental concerns, and growing population are all topics that are widely considered by thinkers in finding optimal solutions to the world’s energy problems, especially environmental crises. Has been busy. Fortunately, most countries around the world recognize the importance and role of different energy sources, especially renewable energy (new) in meeting current and future needs, and widely, in order to expand the use of these indispensable resources, extensive research and principled investments. . Given such fundamental and growing trends in the use of renewable energy and related technologies in industrial and developing countries, in Iran it is necessary to develop strategies and infrastructure programs and principles.
Pollutants from combustion and rising concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and its consequences have left the world with irreversible and threatening changes. Rising global warming, climate change, rising sea levels and, ultimately, the escalation of international conflicts are among these consequences, so all renewable energy is gaining more and more share in the world’s energy supply system. Renewable energies are basically compatible with nature and are not polluting, and because they are renewable, there is no end to them. Other features, such as their dispersion and spread around the world, the need for lower technology, have made renewable energy more attractive, especially for developing countries. That is why in international programs and policies, including the United Nations programs and in the direction of sustainable global development, a special role is played by the supply of energy from sources Newly accepted has been assigned.
In line with the above goals and in order to provide part of the country’s energy and achieve self-sufficiency and resilient economy, the Founders of Powerful Ideas Company has succeeded in identifying areas with clean wind energy capability. One of the identified areas of Herzville Heights is the 20 Seydan watershed, which was proposed to the General Department of Natural Resources of Guilan Province. In line with the policies of the organization and based on the decisions taken in the technical committees of the relevant General Directorate and the headquarters and the Deputy Minister of Forest Affairs, it was decided to join the company due to the proximity of the requested area to the series 5 after appointing a qualified consultant. Non-wood production part of the mentioned series, relying on the rehabilitation and enrichment of empty and sparse areas of forest cover, other non-wood potentials to improve and positive the balance of the project.
For this purpose, the company, by observing all the rules and regulations and observing all the instructions, has attempted to modify and annex the capabilities and capabilities of the mentioned region. In order to prepare this plan, it is necessary that thanks to the efforts and cooperation of Dr. Mohsen Yousefpour Rashti Guilan Province, Engineer Tavakoli, Department of Natural Resources Protection, Guilan Province, Dr. Maziar Razavi, Technical Deputy of Guilan Department of Natural Resources,, Mohammad Reza Abdollahi, Department of Forestry, Rezvan Mohammadpour, Head of Forestry and Parks, Jamshid Aminian The Deputy Minister of Forestry and Project Supervisor, as well as all members of the technical committees of the General Administration and the headquarters of the organization, and especially Dr. Abbas Ali Nobakht, Deputy Minister of Forests, Rangelands and Watershed Management, should be appreciated and thanked.
1 Provide a management program that includes protection of the entire field
2 Identify ecosystem components, identify, introduce and estimate their production capacity and efficiency
3 Preservation of ecosystem and microclimate with the aim of strengthening the role of the protective shield of the series in order to prevent the penetration and destructive effects of hot winds from southern Iran to the north
4 To realize the potential and capabilities of the region, benefit from its benefits in order to manage the project and create employment
5 Improving the situation of livestock farmers in the area
6 Forest development, deforestation and enrichment of sparse areas (increasing the capacity of forest stands)
The total area of the series is 5782 hectares, which includes the areas from the bottom to the top of the dam, and this series is between 49 °, 03 ¢, 05 to 49 °, 33 ¢, 8 and 36 °, 52 ¢, 43 latitude. Is located at 36 °, 44 ¢, 58. This series is between longitude 356312 to 382920 and latitude 4267062 to 4287690 based on the Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system.
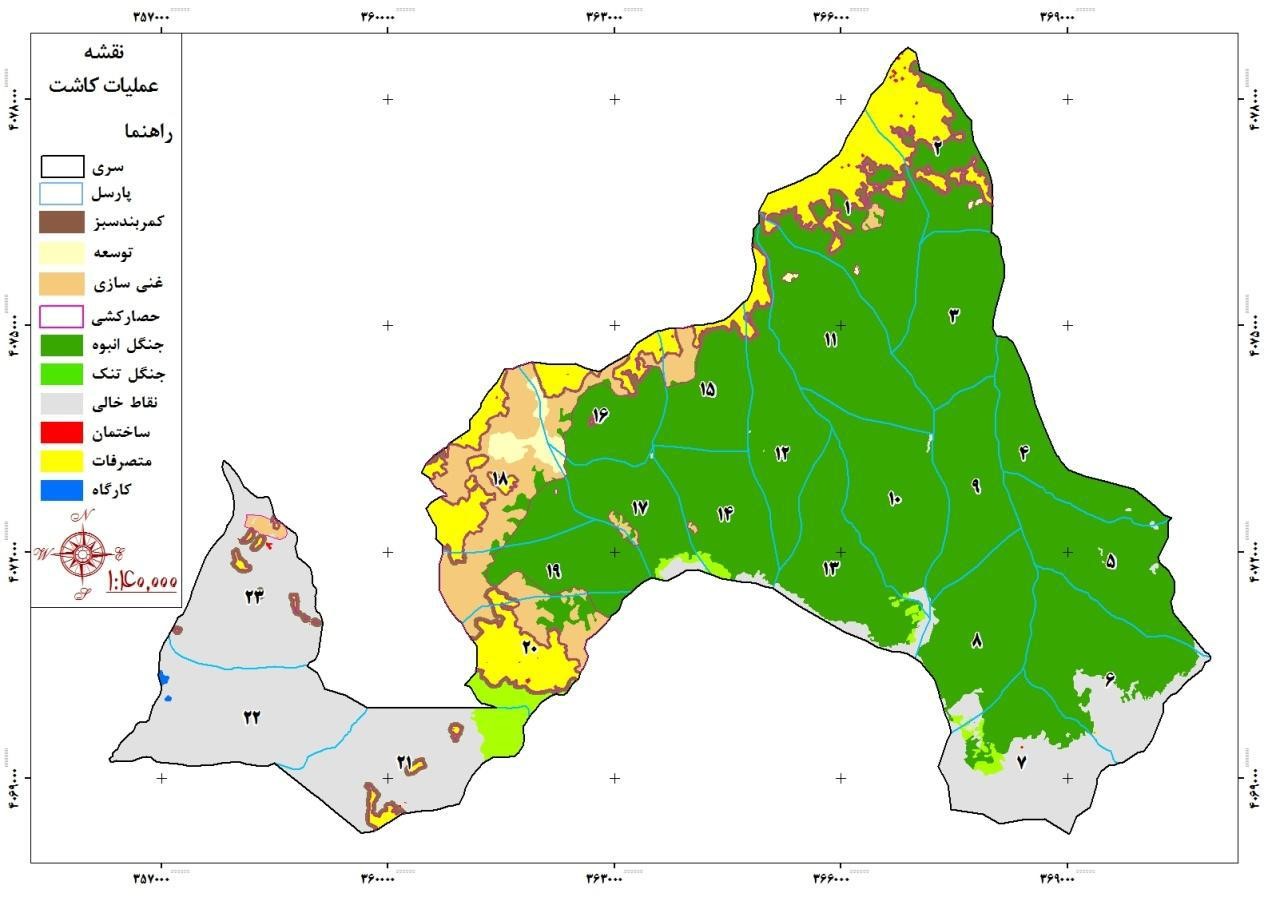
is located. This basin is limited to Sefidrood River from north, northwest and west. It is bounded on the south by Stalkh Bar Mountain and on the east and northeast by the Totkabon River catchment area. This basin borders the Shahroud River catchment area from the east and south. Rudbar city is located on the northern border of the basin. The area of vacant and rangelands is 1305 hectares, the area of protection and support points is 3957 hectares, the area of tourist attractions is 479 hectares, the area of forest reserve is 80 hectares, the area of residential areas and workshops is 7.3 hectares.
Parcels 18, 19 and 20 of the non-wood forestry production plan of 5 series of Oghuzban with an area of 752 hectares, the area of the protection and economic afforestation plan of the company of the founders of a powerful idea.
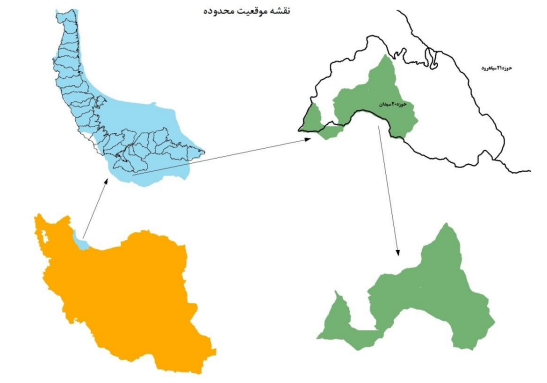
Location map of the forest area plan of 5 Aghuzban series
1.2- History and status of ownership:
The studied secret forests, like other forests in the north of the country, have been under private ownership and smallholders since 1340. Which was managed by employing representatives and supervisors. Series 5 forests of 20 districts of Seydan are considered as non-monolithic forests (non-wood production). No plan has been prepared for the forests of this region so far and no management has been done in the form of written booklets. The initial booklet of the series was prepared in the form of a non-wood production plan in 1997 by the General Department of Natural Resources of Guilan Province. During the process of correcting and reviewing the problems raised by the technical committees and receiving the wind energy request, and after issuing a permit by the relevant organization, the project amendments were put on the agenda while considering the wind energy capability and adjusting its balance.
Forest division:
As mentioned before, the forest of this series is considered as a part of the forests of the 20 Seydan watershed and is located in the protected area of Rudbar city in terms of political division. The study series is divided into 30 plots, the smallest of which is Parcel 524 with an area of 164 hectares and the largest of which is Parcel 500 with an area of 341 hectares. In order to segment the forests of this series, like other forests in the north of the country, red color has been used for parceling in nature. So that at the border of the series, the number of parts with two lines below it (=) and inside the series with a line) – (are marked on the trees, the first digit on the left represents the series and the two digits on the left represent the parcel. 20 to 15 meters, a line _ is marked as a guide line on the trees of the route.Parches 18, 19 and 20, non-timber production forest plan, 5 series, with an area of 752 hectares, range of protection plan and economic afforestation of the company. is.
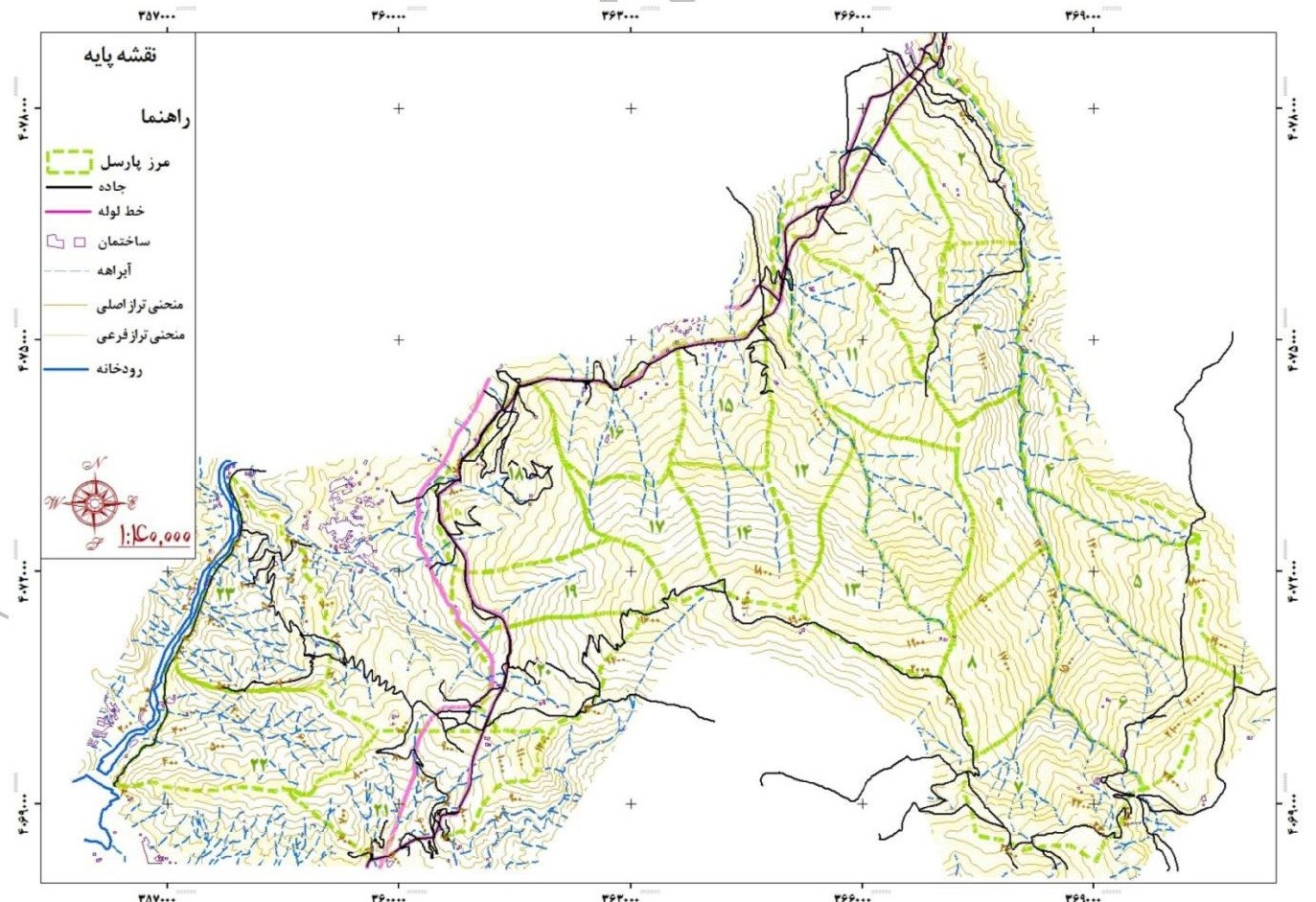
Accessibility:
In order to access the study area and different parts of the series, there are three entrances from different routes of Nasfi rural district, Rudbar city and Manjil city. Series and allows access to this series. Also, a series of roads called the gas pipeline road passes across the lower part of the series (northern border) and connects the above roads. In the western part of this series, the roads branch off from the gas road and in the western part of the series, it stretches to the southwest and ends in the summer area of the skyscraper by passing sections 519, 502, 501 and 518.
Study of elevations:
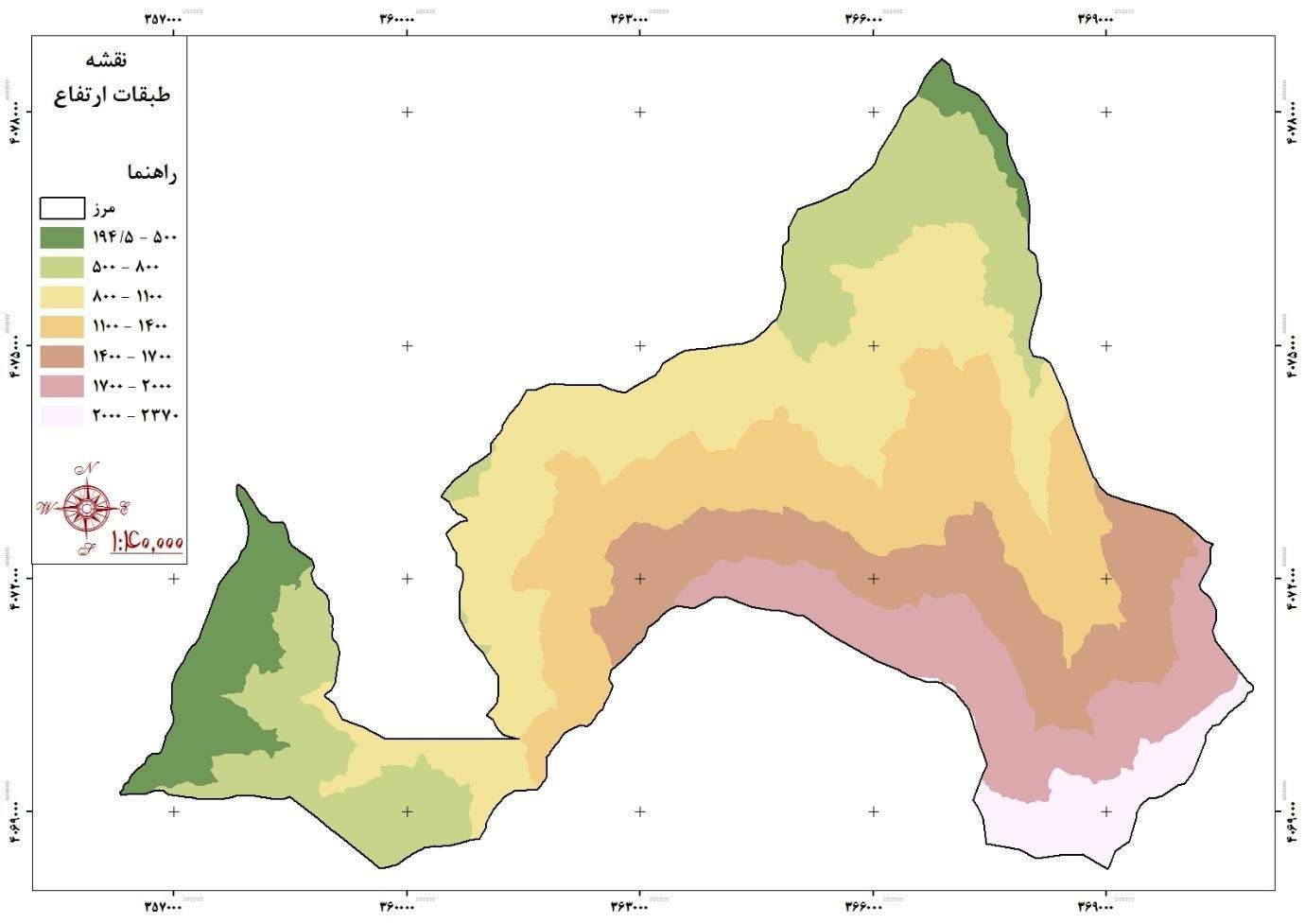
The characteristics of elevation and altitude in each series of 5 columns indicate the climatic position of the basin. The highest point of the basin is 2830 meters above sea level and the lowest point in the basin is the outlet of the basin and its height is 195 meters above sea level.
Topographic maps show natural roughness, that is, height changes between the highest and lowest points. The pattern determines the type of curves and their drawing distance, the type of slope. This means that the small distance of the measure curves from each other indicates a steep slope or precipice. If the distances of the curve lines are higher than each other, it indicates a gentle slope. To study the height and elevation of the study area, use GIS output maps and height distribution with two graphs of level-height compression curve and surface distribution histogram to the specified height. Is.
Study and evaluation of slope characteristics of the region:
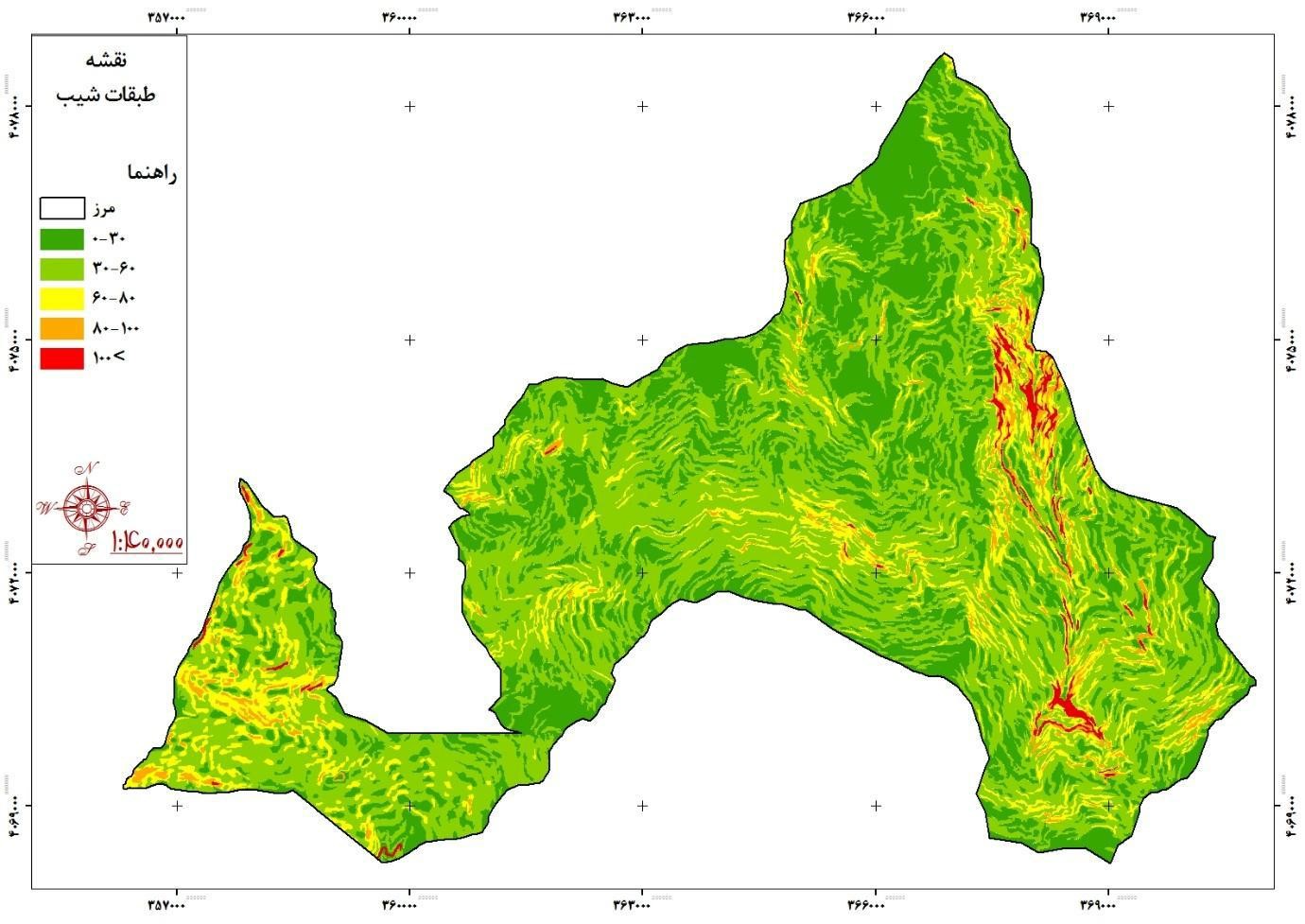
The slope of the basin is studied for evaluations related to the hydrological behavior of the watershed, especially the conversion of precipitation into runoff. Land slope is one of the important factors that control surface flow and concentration time in the river. Soil permeability capacity also depends on the slope. The steeper the slope and the weaker the vegetation, the easier it is to erode.
What is important in relation to slope study in physiographic and topographic studies of a watershed is the distribution of slope relative to its surface and for this purpose a slope map of Rudbar basin has been prepared. GIS software is used in scale 1: 22250 and appropriate classes are determined.
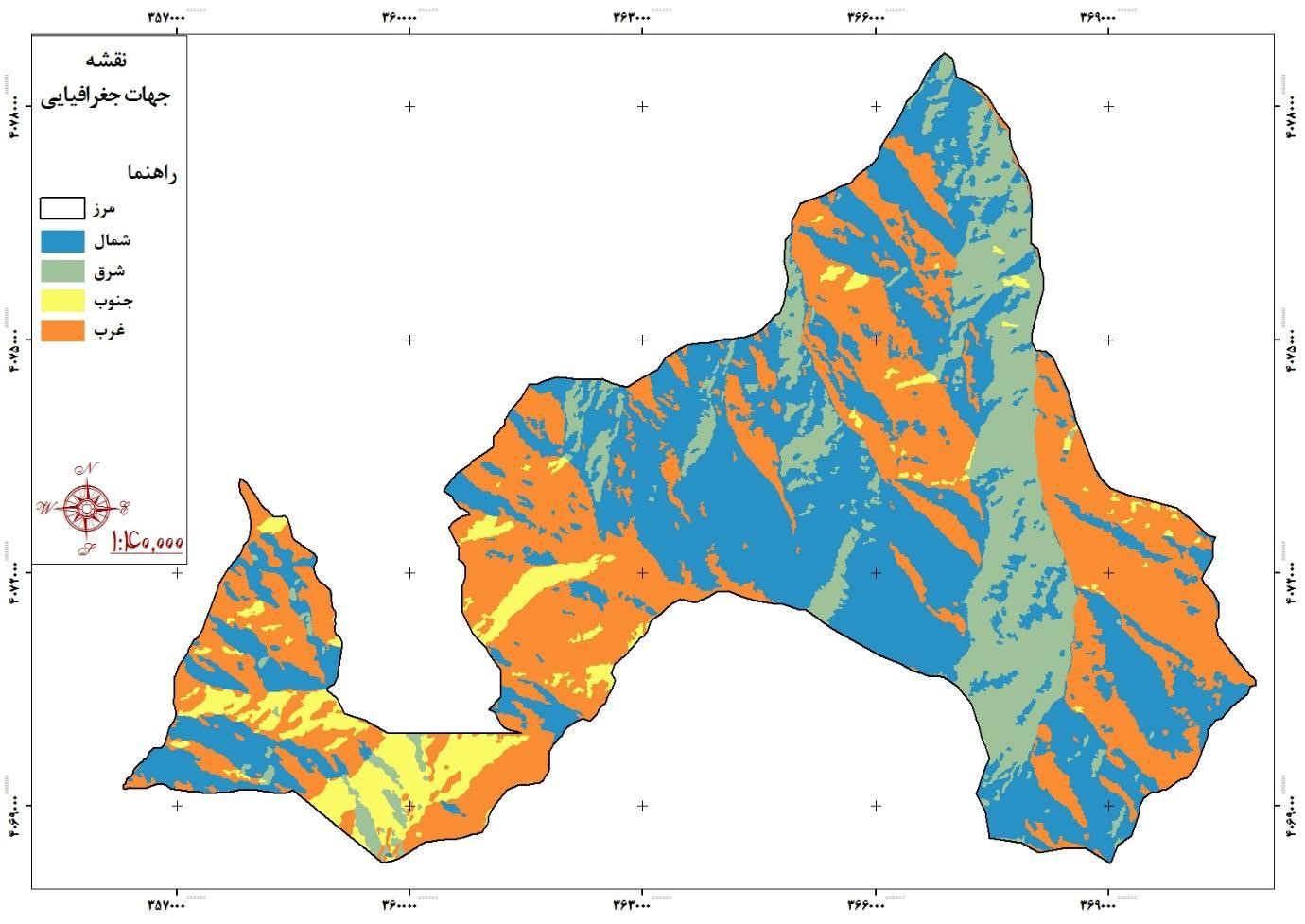
Basin slope direction:
The slope factor is important in terms of its impact on some hydrological processes, snowmelt, vegetation diversity, etc. in watersheds. The slope direction of the basin can be measured and described in different ways. One method is to consider only the general direction of the basin, for example, a basin or sub-basin of it may be located on the northern slopes of a mountain range, in which case it is clear that the direction of its slope is north. Four directions (north, east, south and west) or eight directions may be considered more precisely to determine the direction of the basin. In watershed management studies, in terms of the effect that the direction of the basin slopes has on the type of soil erosion, it is necessary to prepare a map for the slope of the basin.
Given that Iran is located in the northern hemisphere and in the southwest of Asia. In the northern hemisphere, the south and west directions are exposed to sunlight for a longer period of time than the north and east directions, and are therefore warmer. Therefore, more radiation and more heat causes evapotranspiration to increase in the surface of watersheds and decreases soil moisture.
Another important effect of slope direction is the intensity of snowmelt. In the south and west directions, the speed of snow melting is faster than other directions. Therefore, in the south and west directions, snowmelt occurs during winter and early spring, but in the north and east directions, snowmelt occurs mainly in spring and due to sudden heat, floods are more likely to occur. GIS software analysis at a scale of 1: 22250 was used to prepare the slope directions map of the study basin.